Don't Disable Zoom
For users with low vision, the ability to zoom or resize text is essential for readability. Users should be able to resize text - using Cmd + on MacOS, or Ctrl + on Windows - up to 200% without loss of content or functionality.
Viewport configuration
The viewport is the visible area of the web page within the browser's window. The <meta name="viewport"> tag controls how your page scales and responds on different screen sizes.
To support both zooming and responsive layouts make sure to have width=device-width, initial-scale=1 in your viewport meta tag. FastHTML sets these by default in core.py and includes viewport-fit=cover, which renders content behind the notch on mobile devices like iPhones.
# https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/fasthtml/blob/acb190bbe4c3661850de637b4c17bfc2f7ff14b3/fasthtml/core.py#L455
viewport = Meta(name="viewport", content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, viewport-fit=cover")width=device-width: sets the layout viewport width to match the physical screen width.initial-scale=1: sets the initial zoom level when the page first loads.
Don't prevent user scaling
Avoid using user-scalable=0, user-scalable=no, or maximum-scale=1.
Blocking zoom directly harms people who rely on it to read or interact with your content. Users with low vision may be unable to enlarge text to a comfortable size forcing them to leave your site entirely.
Designing for zoom and resizing
Responsive layouts are key to supporting zoom. CSS frameworks like Pico CSS (commonly used with FastHTML) adapt well when paired with:
- Relative units (rem, em, %) instead of fixed pixels.
- Flexible containers that grow or wrap as content scales.
- Avoidance of fixed heights/widths that cause clipping.
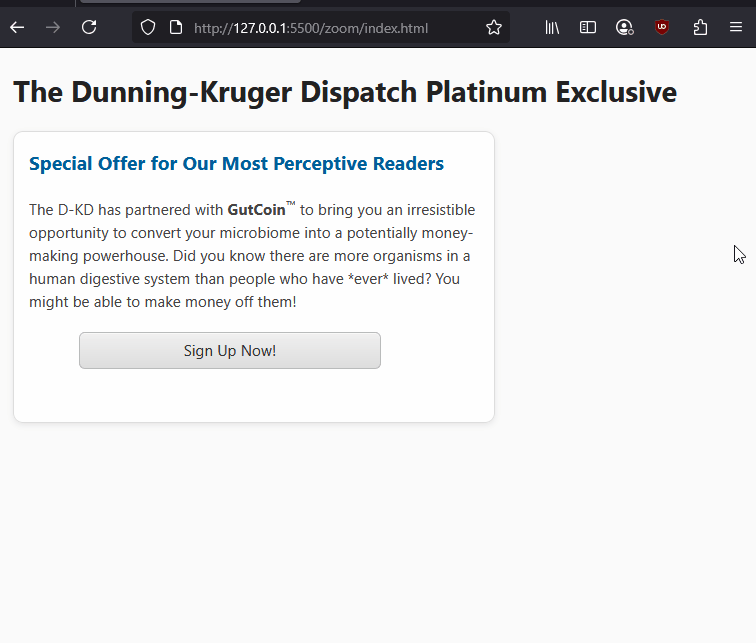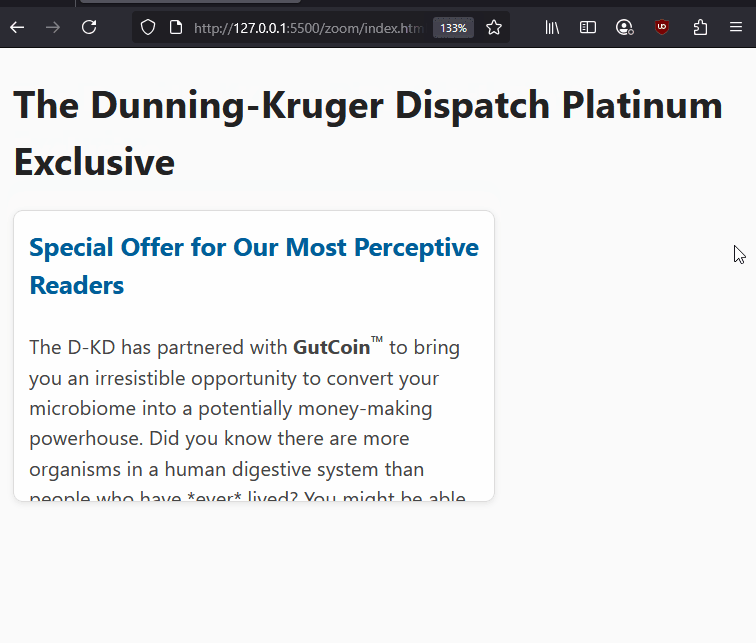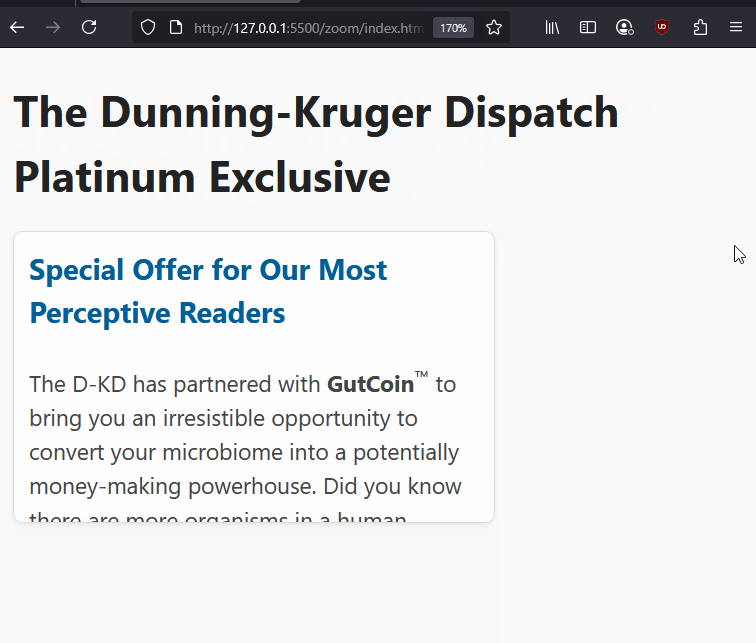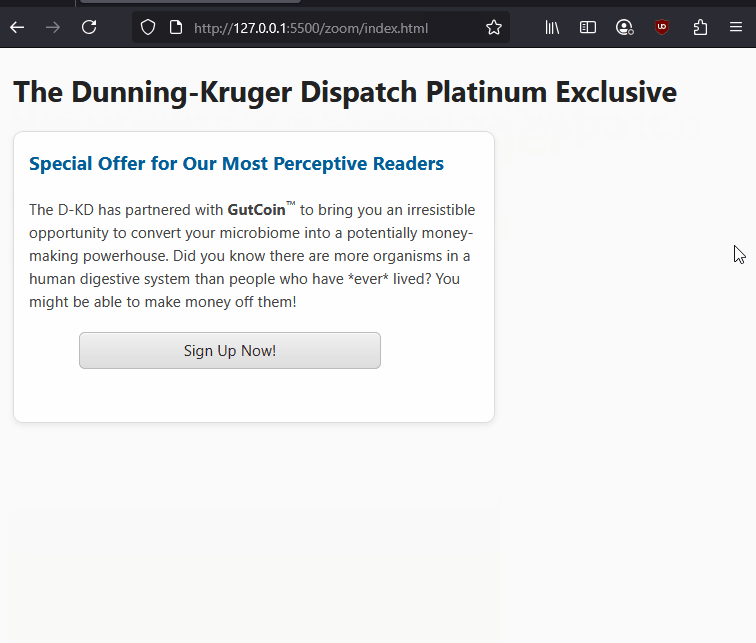
Here is an example of fixed widths preventing proper resizing on zoomed to 200% in Firefox.
WCAG Success Criteria
This WCAG success criterion relates to the accessibility topics covered in this post.
1.4.4 Resize Text (AA): - People should be able to resize page text up to 200% without losing content or functionality. They should be able to do this without requiring additional assistive technologies.